تاثیر سورفکتانت ها بر رفتار حمام Ni - P و ایجاد پوششهای کامپوزیتی الکترولس Ni - P - TiC
- مقالات علمی
- بازدید: 1303
erf
ختاثیر سورفکتانت ها بر رفتار حمام Ni - P و ایجاد پوششهای کامپوزیتی الکترولس Ni - P - TiC
کارهای مهم: ویژگیهای حمام Ni - P با استفاده از سه نوع سورفاکتانت مورد بررسی قرار میگیرند. خواص Wetting حمام Ni - P در tic، فولاد W۳۰۲ و پوشش Ni - P تعیین میشوند. پتانسیل سنجی و اندازه ذرات of های Ni - P - tic اندازهگیری میشوند. پوششهای مرکب Ni - P - tic با موفقیت ایجاد شدند. مقدار of که در پوشش گنجانده شده برای هر یک از study مطالعه حاضر یک بررسی سیستماتیک در مورد تاثیر سه نوع سورفکتانت آنیونی (آنیونی: sdbs، کاتیونی: CTAB و غیر یونی: PVP)بر رفتار پوششهای الکترولس Ni - P حاوی نانو ذره، و تشکیل پوشش کامپوزیتی Ni - P - tic است. تاثیر سورفکتانت ها را می توان در پدیده سطحی، به عبارت دیگر wetting و رفتار electrokinetic در طول شکلگیری پوشش مشاهده کرد. خواص wetting حمام پوشش با استفاده از روش قطره چسبیده مورد بررسی قرار گرفت که نشاندهنده بهبود مرطوب در هر سه زیر لایه (لایههای فولاد W۳۰۲، tic، Ni - P)در مورد سورفکتانت آنیونی و کاتیونی بود. اندازهگیری پتانسیل سنجی نشاندهنده کاهش پایداری در حمام Ni - P در مقایسه با محیط آب مقطر است که منجر به تجمع ذرات tic میشود. تجمع ذرات با اندازه ذرات کمتر از ۱۰۰ نانومتر توسط هر سه نوع سورفکتانت (۱ گرم بر لیتر)در آب مقطر به دست آمد؛ با این حال تنها آگلومره های بزرگتر در حمام Ni - P اندازهگیری شدند. در نهایت، پوششهای کامپوزیتی Ni - P - tic بر روی بستر فولادی ساخته شدند. بررسی سطح مقطع پوششها نشان داد که بالاترین مقدار of (۰.۵۳ wt. % و ۰.۵۲ wt. در ماتریس Ni - P با استفاده از ۰.۱ g / L CTAB و ۰.۱ g / L PVP به ترتیب در ماتریس Ni - P و ۰.۱ g / L PVP ترکیب شد.
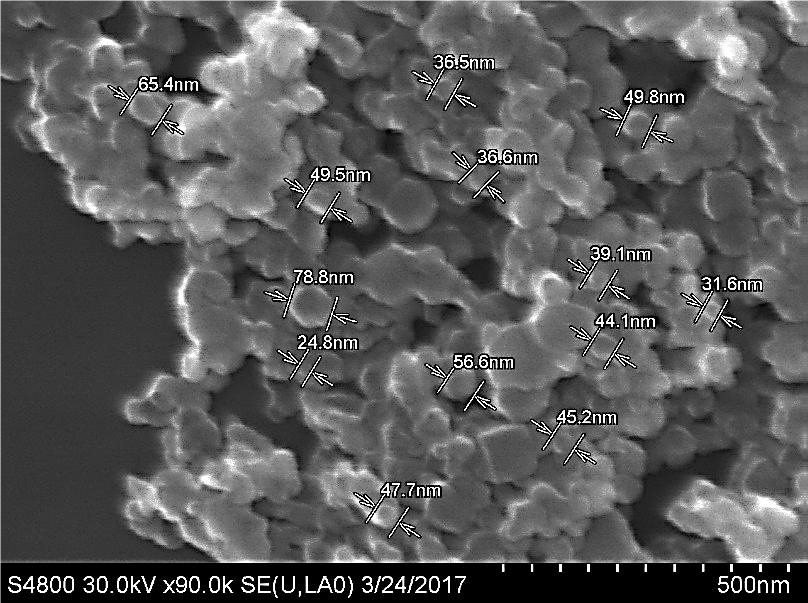

تصویر میکروسکوپ الکترونی روبشی تیتانیوم دی اکسید
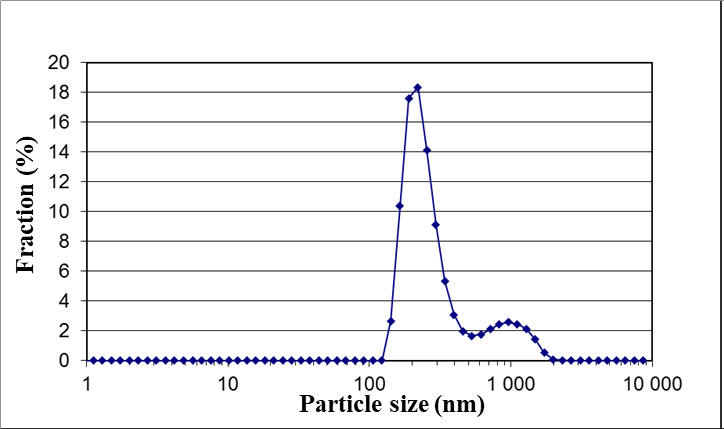
شکل 1: متوسط سایز ذرات کاربید تیتانیوم
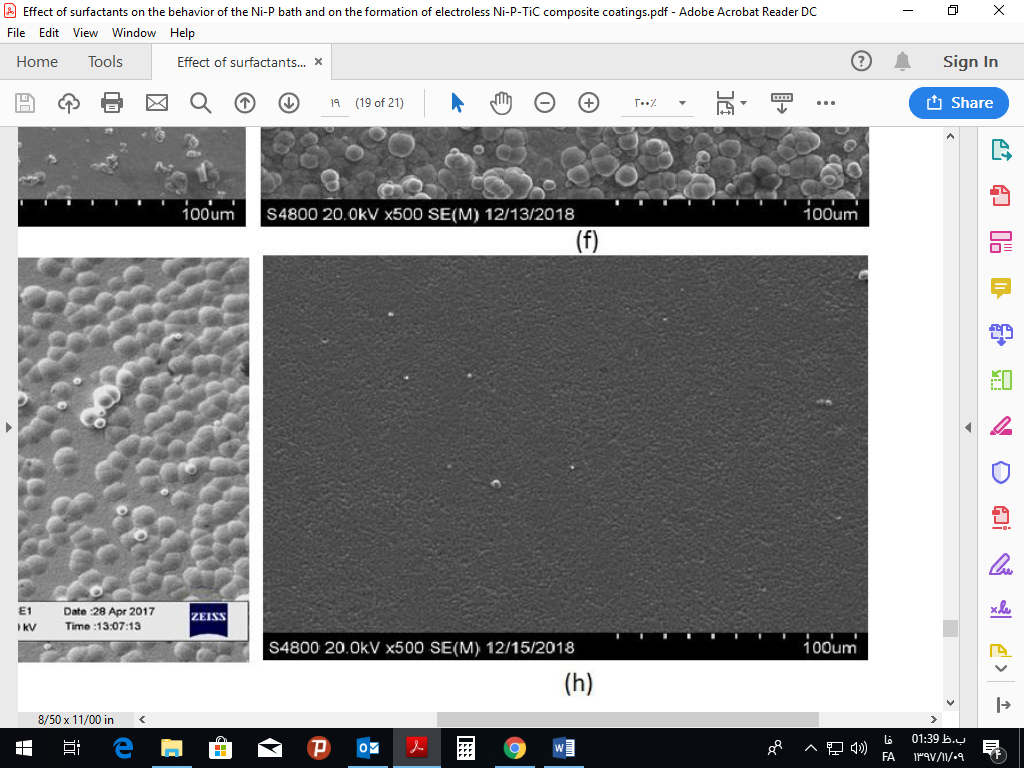
شکل 2: تصویر میکروسکوپ الکترونی روبشی از برش عرضی
References
[1] I. Apachitei, J. Duszczyk, L. Katgerman, P.J.B. Overkamp. Electroless Ni–P Composite coatings: The effect of heat treatment on the microhardness of substrate and coating - Structure and properties. Scripta Mater. 38 (9) (1998) pp. 1347-1353
[2] J. Sudagar, J. Lian, W. Sha. Electroless nickel, alloy, composite and nano coatings – A critical review. J. Alloy. Cmpd. 571 (2013) pp. 183–204
[3] J.N. Balaraju, T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, S.K. Seshadri. Electroless Ni–P composite coatings J. Appl. Electrochem. 33 (2003) pp. 807–816
[4] C.S. Chang, K.H. Hou, M.D. Ger, C.K. Chung, J.F. Lin. Effects of annealing temperature on microstructure, surface roughness, mechanical and tribological properties of Ni–P and Ni–P/SiC films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 288 (2016) pp. 135-143
[5] S. H. Hashemi, A. Ashrafi. Characterisations of low phosphorus electroless Ni and composite electroless Ni-P-SiC coatings on A356 aluminium alloy. Transaction of the IMF. 96 (1) (2018) pp. 52–56
Highlights•Ni-P bath characteristics are investigated using three types of surfactants. Wetting properties of Ni-P baths on TiC, W302 steel and Ni-P coating are determined.•Zeta potential and particle size of Ni-P-TiC dispersions are measured.•Ni-P-TiC composite coatings were successfully created.•The amount of TiC incorporated into the coating is determined for each surfactant. Abstract The present study is a systematic investigation into the effect of three different types of surfactants (anionic: SDBS, cationic: CTAB, and non-ionic: PVP) on the behaviour of electroless Ni-P baths containing TiC nanoparticles, and on the formation of Ni-P-TiC composite coatings. The effect of surfactants can be observed in the interfacial phenomena, i.e. wetting and electrokinetic behaviour during the formation of the coating. The wetting properties of the coating bath were investigated by the sessile drop method, which revealed the wetting improvement on all three substrates (W302 steel, TiC, Ni-P coating substrates) in the case of the anionic and cationic surfactant. The Zeta potential measurement showed a stability decrease in Ni-P bath compared to the distilled water medium, which led to the agglomeration of the TiC particles. TiC agglomerate size below 100 nm was achieved by all three types of surfactant (1 g/L) in distilled water; however, only larger agglomerates were measured in the Ni-P bath. Finally, the Ni-P-TiC composite coatings on steel substrate were created. The investigation of the cross-section of the coatings revealed that, the highest amount of TiC (0.53 wt.% and 0.52 wt.%) was incorporated in the Ni-P matrix with the use of 0.1 g/L CTAB and 0.1 g/L PVP respectively, although these particles formed larger agglomerates
نویسنده این مطلب
محقق واحد پژوهش و گسترش
|
Prepared by research and development Unit Of Jalapardazan (JP) By MRH Education: Master Of Analytical chemistry |
تهیه شده در واحد پژوهش و گسترش جلاپردازان پرشیا (JP) گردآوری و ترجمه: م ر ح تحصیلات: کارشناسی ارشد شیمی تجزیه |